Lymphatic Interventions
Lymphatic Interventions
Lymphatic Interventions are medical procedures aimed at diagnosing and treating disorders of the lymphatic system, which plays a crucial role in immune function and fluid balance in the body. Here are explanations of three specific lymphatic interventions:
Lymphangiography:
- Lymphangiography is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to visualize the lymphatic vessels and identify abnormalities or blockages within the lymphatic system.
- During lymphangiography, a contrast dye is injected into the lymphatic vessels, typically in the foot or hand. The dye travels through the lymphatic system, allowing radiologists to capture X-ray images or perform other imaging modalities, such as CT or MRI, to visualize the lymphatic vessels and identify any abnormalities.
- Lymphangiography can help diagnose conditions such as lymphedema (swelling due to lymphatic fluid accumulation), lymphatic malformations, lymphatic leaks, and lymph node involvement in cancer staging.
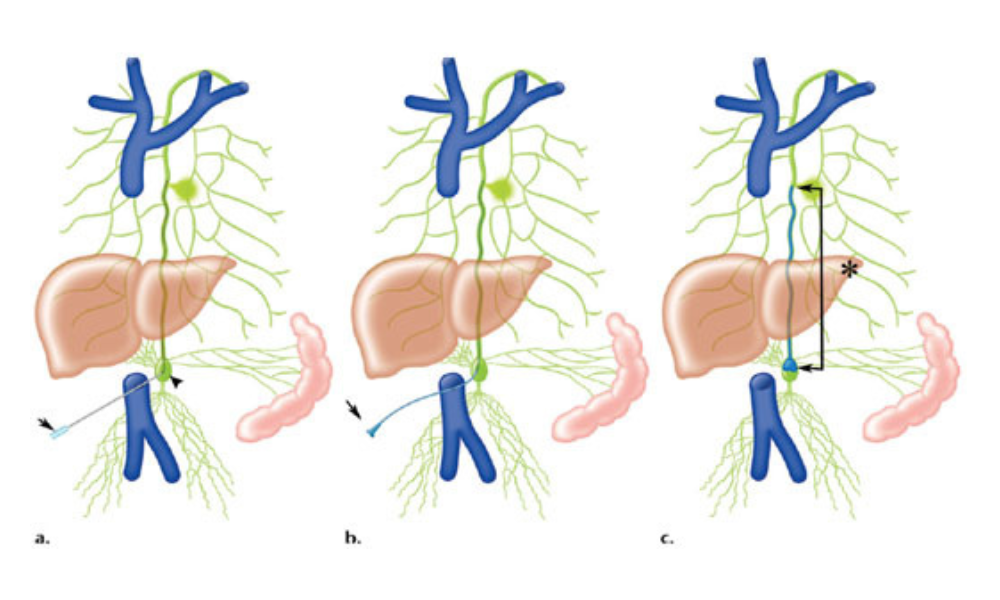
Thoracic Duct Cannulation:
- The thoracic duct is the largest lymphatic vessel in the body, responsible for draining lymphatic fluid from the lower body, left upper body, and left side of the head and neck into the bloodstream.
- Thoracic duct cannulation is a procedure used to access the thoracic duct directly, typically for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
- During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a lymphatic vessel, often through a small incision or needle puncture, and advanced into the thoracic duct under imaging guidance, such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound.
- Thoracic duct cannulation can be used for various purposes, including collecting lymphatic fluid for analysis, injecting contrast dye for lymphangiography, or delivering medications or embolic agents for therapeutic purposes.
Thoracic Duct Embolization:
- Thoracic duct embolization is a therapeutic procedure used to treat conditions such as chylous leaks, in which lymphatic fluid leaks into the chest or abdominal cavity, leading to symptoms such as fluid accumulation (chylous effusion)


